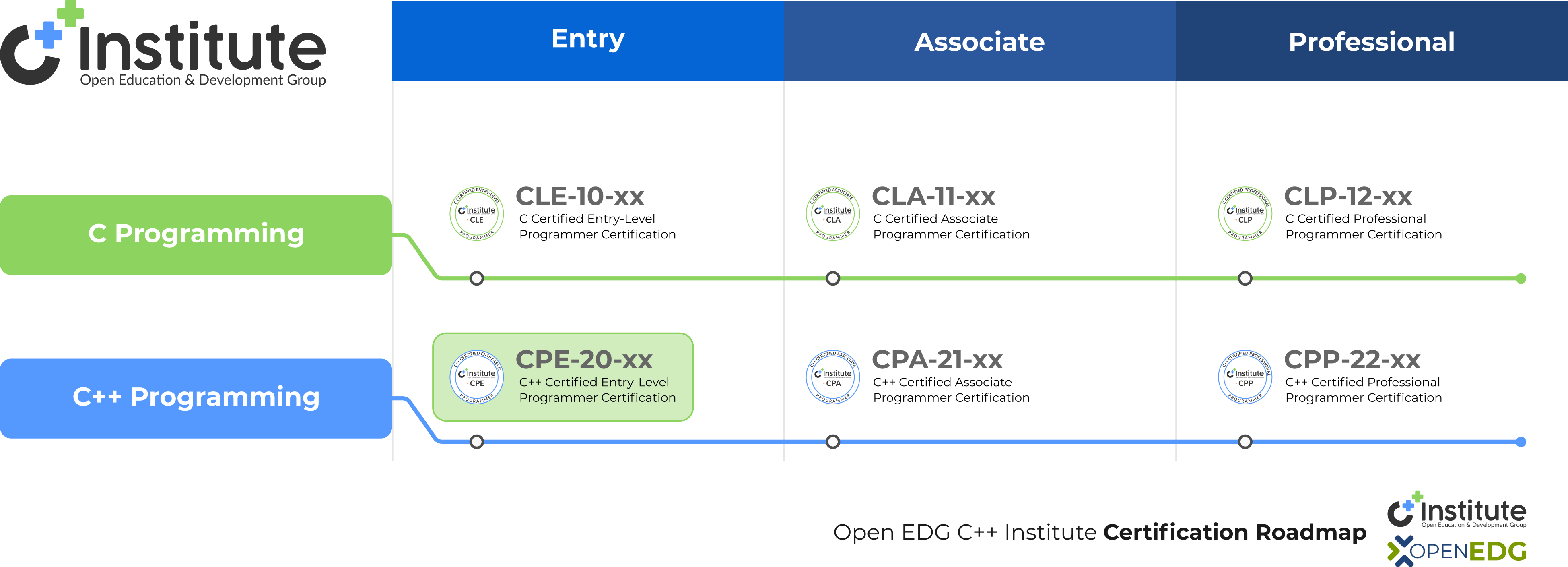
The CPE – C++ Certified Entry-Level Programmer certification is the perfect starting point for anyone beginning a career in software development, C++ programming, or related fields such as low-level and middle-level programming. It validates your grasp of essential programming concepts, including compilation, variables, data types, typecasting, operators, control flow, arrays, pointers, structures, and the runtime environment.
By earning the CPE certification, you gain a valuable competitive edge and lay the groundwork for future success – including progression to the CPA – C++ Certified Associate Programmer certification and more advanced professional opportunities.

To earn the CPE – C++ Certified Entry-Level Programmer certification, a candidate should demonstrate the ability to apply core programming concepts and write basic C++ programs. Key knowledge areas and skills include:
Exam name:
CPE – C++ Certified Entry-Level Programmer
Exam code:
CPE-20-0x (x denotes the exam version)
Associated certifications:
CPA – C++ Certified Associate Programmer
CPP – C++ Certified Professional Programmer
Prerequisites:
None
Exam version:
CPE-20-01 (Active)
Duration:
45 minutes (exam) + approx. 5 minutes (Non-Disclosure Agreement/Tutorial)
Number of questions:
30
Format:
Single-choice questions, multiple-choice questions, gap fill, drag & drop
Passing score:
70%
Cost:
USD 69 (Exam)
USD 86 (Exam + Retake)
Languages:
English
Learning resources:
C++ Essentials 1 – Cisco Networking Academy (Go to Cisco NetAcad)
C++ Essentials 1 (Beginner) – OpenEDG Learning Platform (Go to OpenEDG Edube)
Exam delivery channel:
Exam policies:
Click here to go to Exam Policies
Exam syllabus:
Click here to go to Exam Syllabus
Exam Vouchers
Exam vouchers available through the OpenEDG Voucher Store
The CPE certification exam assesses foundational skills in C++ programming. It verifies the candidate’s ability to write simple programs, apply basic programming constructs, understand fundamental concepts, and use standard library elements. The exam focuses on syntax, program logic, data manipulation, functions, pointers, structures, and strings.
The CPE exam consists of 30 questions (items), each carrying a different score value based on its complexity and objective. The maximum total score is 120 points, which is then normalized and converted into a percentage. To pass, a candidate must achieve a cumulative score of 70% or higher across all questions – the result is based on the total points earned, not on a simple average of scores per exam block.
The scoring system is based on psychometric analysis, where each question is assigned a weight and point value reflecting its difficulty and importance. This ensures that the exam measures knowledge and skills fairly, with the final score representing the total points earned across all questions, rather than a simple count of correct answers.
Block 1 – Syntax, Literals, and Operators
(Exam items: 9 | Weight: 28%)
Block 2 – Flow Control and Functions
(Exam items: 8 | Weight: 28%)
Block 3 – Vectors and Pointers
(Exam items: 7 | Weight: 24%)
Block 4 – Structures and Strings
(Exam items: 6 | Weight: 20%)
A Minimally Qualified Candidate (MQC) for the CPE – C++ Certified Entry-Level Programmer certification understands the fundamental concepts of C++ programming and can apply them to write simple, correct programs that demonstrate practical use of core language features.
The candidate demonstrates knowledge of C++ syntax, data types, operators, and input/output mechanisms (Block 1), and is able to control program flow using conditional statements, loops, and functions, including basic recursion and parameter passing (Block 2). They can declare, initialize, and manipulate vectors, arrays, and pointers, and manage dynamic memory safely (Block 3). Additionally, the candidate is capable of defining and using structures and strings, performing basic operations, and organizing simple data within a program (Block 4).
The MQC is prepared to advance to higher-level certifications and apply entry-level C++ skills in practical programming tasks.
Last updated: July 22, 2025
First published: November 15, 2012
Aligned with Exam CPE-20-01